Internal Link Building 101: The Overlooked Strategy That Boosts SEO Like Magic
Internal link building might not sound as exciting as scoring a high-DA backlink from a major publication, but if you’re ignoring it, you’re leaving serious SEO potential on the table. When used correctly, internal linking does more than just help users find related content—it strengthens your site’s architecture, boosts topical authority, increases crawlability, and keeps visitors engaged longer.
In this guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about internal linking—from how it works to why it’s often overlooked, and exactly how to build a powerful internal link strategy for your website.

📌 What Is Internal Linking, Anyway?
Let’s start with the basics.
Internal links are hyperlinks that point from one page on your domain to another page on the same domain. For example, a blog post about SEO basics might link to a separate article about keyword research.
These links help:
- Guide users to relevant content
- Establish a logical site structure
- Distribute page authority across your domain
- Help search engines understand how your pages are related
There are different types of internal links:
- Navigational links: like those in your site’s menu or footer
- Contextual links: placed within the body of a page or post
- Image links: when you use images as links between pages
- Breadcrumb links: showing the path to the current page (e.g., Home > Blog > SEO)
🧠 Why Internal Links Matter for SEO
🔍 1. Helps Search Engines Crawl Your Site
Internal links allow Google’s bots to discover and crawl pages efficiently. If a page on your site isn’t linked to from anywhere else, it might be invisible to search engines—even if it’s published and indexed.
💪 2. Passes Authority (Link Equity)
When you link from a high-authority page to a newer or lower-authority page on your site, you pass some of that page’s value (called link equity or link juice) to the other. Over time, this helps your important pages rank higher.
📚 3. Boosts Topical Relevance and Authority
Linking related content builds topical clusters, which tells Google your site is deeply knowledgeable about a subject. This improves your E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust).
📈 4. Increases Time-on-Site and Reduces Bounce Rate
By linking to helpful content naturally within your posts, users are more likely to click through and stay on your site longer. This improves engagement signals—another positive ranking factor.
💡 5. Helps Guide Visitors Where You Want Them
Want people to check out a specific service page? Or subscribe to a newsletter? Internal links can drive traffic exactly where you want it to go—without being pushy.
🧱 The 4 Pillars of a Solid Internal Link Strategy

Building a good internal linking structure is more than just adding links randomly throughout your site. These four core principles should guide your strategy:
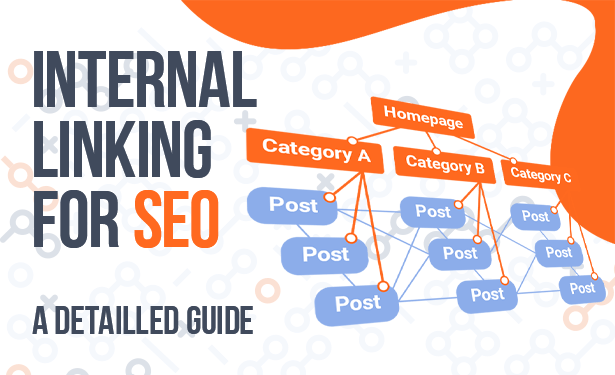
1. Hierarchy Matters
Create a logical structure. Think of your website like a pyramid:
- The homepage sits at the top
- Main category pages underneath it
- Individual blog posts or product pages beneath that
Each level should link downward and upward. No page should be more than 3 clicks deep from the homepage.
2. Use Anchor Text Strategically
The clickable text in a hyperlink is called anchor text. Google uses it to understand what the linked page is about.
Do this:
- Use descriptive, relevant keywords in your anchor text
- Keep it natural (avoid keyword stuffing)
- Vary your anchor text across pages
Avoid this:
- Using generic text like “click here”
- Repeating the same anchor over and over
3. Link Related Content Together
Use internal links to create topic clusters. For example, a post on “Email Marketing” should link to:
- Email subject line tips
- List-building strategies
- Best email marketing platforms
This builds topical authority and improves semantic SEO.
4. Prioritize Key Pages
Identify your money pages—the ones that drive sales, leads, or conversions—and point multiple internal links toward them. Use internal linking to strategically push traffic (and SEO value) toward those pages.
🔄 When and Where to Add Internal Links
Here’s where to look for opportunities:
| Location | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Blog Posts | Link to other posts or pillar content that expand on a topic |
| Product Descriptions | Link to related items, FAQ pages, shipping info, or category pages |
| Homepage | Feature top categories, trending articles, or seasonal products |
| Category Pages | Link to best-sellers, reviews, or tutorials within that category |
| Footer | Add important but less-trafficked links (like privacy, sitemap, contact, etc.) |
✏️ Pro Tip: When you publish a new blog post, go back to old posts and add links to it—not just from it.
🔧 How to Build an Internal Linking Strategy (Step-by-Step)
✅ Step 1: Perform a Site Audit
Use a tool like:
- Ahrefs Site Audit
- Screaming Frog
- SEMrush
Look for:
- Orphaned pages (no internal links)
- Overlinked pages (too many internal links diluting value)
- Broken internal links
- Pages with few inbound links
✅ Step 2: Identify Important Pages
Your target pages might be:
- Product or service pages
- Pillar content
- High-converting blog posts
- Pages that need a rankings boost
Create a list of 10–20 pages you want to drive more traffic to.
✅ Step 3: Add Contextual Links Naturally
Go through related blog posts and add internal links to your target pages using relevant anchor text. Only link where it makes sense—don’t force it.
✅ Step 4: Keep Track in a Spreadsheet
Create a simple table to track:
| Source Page | Target Page | Anchor Text | Date Added |
|---|---|---|---|
| /blog/seo-tips | /seo-services | SEO consulting | July 8, 2025 |
This keeps your structure organized and helps you avoid duplicates.
✅ Step 5: Revisit and Refresh
Internal linking isn’t a one-and-done task. Revisit every few months:
- Add new links to fresh content
- Remove outdated or broken ones
- Adjust anchor text to match evolving search intent
🚫 Common Internal Linking Mistakes to Avoid
| ❌ Mistake | ✅ Better Approach |
|---|---|
| Linking every instance of a keyword | Use a few well-placed links per page—quality over quantity. |
| Using the same anchor text every time | Vary your anchors to look natural and capture different search intents. |
| Linking to irrelevant content | Always link to content that’s genuinely helpful and topically related. |
| Forgetting about orphan pages | Use audits to find pages with no inbound internal links. |
| Ignoring link placement | Place links early in the content if possible—they get more clicks. |
🧊 Tools That Help With Internal Link Building
| Tool | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Yoast SEO | Suggests internal links as you write (WordPress only) |
| Link Whisper | Auto-suggests internal links based on your content |
| Ahrefs Site Audit | Identifies orphaned pages, internal redirect chains, and broken links |
| Screaming Frog | Crawls your site to show every internal link on every page |
| Surfer SEO | Helps with optimizing content clusters and linking for topical SEO |
📊 Internal Linking Best Practices (Quick Table
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Use clear, relevant anchor text | Don’t use “click here” or vague phrases |
| Link to new pages from old ones | Don’t forget to update your older content |
| Create topic clusters | Don’t link unrelated content together |
| Link early in the content where possible | Don’t hide links at the bottom if they provide value |
| Audit and update regularly | Don’t “set and forget” your internal linking structure |
❓Internal Linking FAQ
What is an orphan page?
An orphan page is a page on your site that has no internal links pointing to it. Google may struggle to find or crawl it.
How many internal links should I include per page?
There’s no strict number, but 3–10 internal links per 1,000 words is a good general range. Prioritize relevance and user value.
Can internal links improve SEO rankings?
Absolutely. Internal links help distribute page authority and signal relevance to search engines, improving keyword rankings and traffic.
Is internal linking better than external linking?
They’re both important. Internal linking gives you control, while external backlinks give you authority. You need both.
Should I open internal links in a new tab?
Generally, no. Keep users on the same tab for better flow unless the link is to a PDF or external resource.
Can too many internal links hurt SEO?
Yes—if overdone, they can dilute page authority or confuse search engines. Always prioritize quality over quantity.

🎯 Final Thoughts: Why Internal Linking Deserves More Love
Internal link building isn’t flashy, but it’s one of the most effective and most overlooked strategies in SEO.
Done right, it:
- Increases page visibility
- Spreads authority to pages that need a boost
- Improves user experience
- Builds content clusters for better topical relevance
And the best part? You have complete control over your internal link strategy. No outreach. No waiting. Just smart architecture and thoughtful linking.
So next time you hit publish on a blog post, don’t just promote it—link it.

